Chemical Hazard PPE and How to Protect Workers From Poisons

Which PPE Materials Work Best for Chemical Splash From Poisons?
Personal protective equipment (PPE) materials used to protect against chemical splashes must be resistant to the specific chemicals being handled. Different poisons react differently with protective materials, so selection should always be based on information provided in the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
Common PPE materials used for chemical splash protection include nitrile, neoprene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyethylene, which help prevent liquids from penetrating gloves, aprons, or suits. Face shields, goggles, and chemical-resistant clothing provide additional protection by blocking splashes from contacting the eyes, face, and skin. When PPE materials are chosen to match the chemical hazard, they reduce exposure risk and support safe handling practices.
Why Do Workplaces Need Personal Protective Equipment for Chemical Hazards?
Poisons and hazardous chemicals are present in nearly every industry. Farmers and agricultural workers may encounter pesticides; lab employees and scientists may mix, study, and experiment with solvents and new compounds; and construction workers may be at risk for inhaling paint and dangerous dust particles.
Fortunately, proper personal protective equipment (PPE) can protect against dangerous chemicals, airborne hazards, and other poisons present on jobsites. To keep workers safe, it's important to know when chemical hazard PPE may be required, which types should be used, and how it can help keep employees safe. Employers can also reduce risk by conducting a documented hazard assessment and reinforcing PPE requirements with signage and training.
How Can Employees Become Exposed to Poisons and Other Hazards?
Workers are generally exposed to toxic chemicals and other poisons in one of three ways:
- Skin and eye contact: This occurs when an employee (not wearing proper PPE) comes into contact with a hazardous material or chemical. This may cause numerous symptoms, including skin or eye irritation, rashes, and burns.
- Inhaling hazardous vapors: An employee may breathe in toxic fumes while working in an area without proper ventilation or while working without a respirator. Doing so may lead to respiratory illnesses or lung cancer.
- Swallowing toxic chemicals: This may happen when hands or foods are contaminated, and poisons are ingested. Swallowing poisonous materials may lead to a variety of side effects, including dizziness, skin irritation, organ damage, and more.
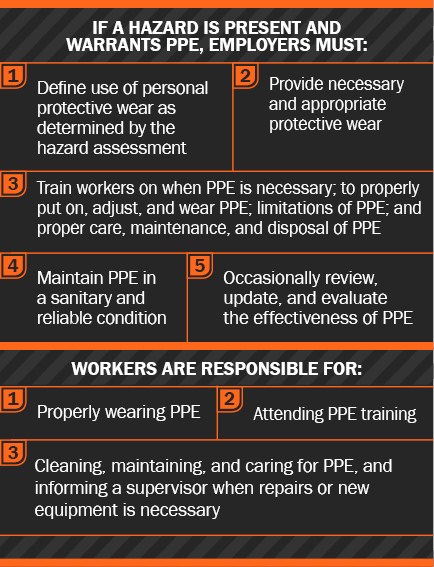 What Does OSHA Require for Chemical Hazard PPE?
What Does OSHA Require for Chemical Hazard PPE?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has a variety of requirements regarding PPE in the workplace, many of which vary by industry. (Shipyards have their own standard, for instance, as does construction and demolition work.) General requirements that apply to most workplaces may be found in 29 CFR 1910.132.
OSHA's PPE requirements direct employers to conduct a hazard assessment of their workplaces and provide proper PPE accordingly. This hazard assessment is a key step in determining when chemical hazard PPE is needed and what level of protection is required.
How Do Employers Select Chemical Hazard PPE Using a Hazard Assessment?
Each container of hazardous chemicals should be labeled, and should have a detailed safety data sheet (SDS) available to describe its hazards and the appropriate precautions. These two elements are required in OSHA's HazCom 2012 standard.
Container labels include the name of the material and information about the hazards that material may pose. An SDS includes more extensive information employees may need to know when working with dangerous chemicals, including first-aid measures and any required PPE.
How Does PPE Protect Workers From Poisons and Hazardous Chemicals?
Proper PPE comes in many forms and protects against numerous hazardous chemicals. The following types of PPE are especially helpful in protecting against poisons and other hazards:
Foot and Leg Protection: Durable boots can protect against chemicals that have spilled, including paint and pesticides. Employees may wear shoe covers to prevent contact with a contaminated surface. Foot protection should be compliant with the ANSI Z41.1 standard, which sets the criteria for testing, selecting, maintaining, and using foot protection in American workplaces.
Hand Protection: Gloves can protect employees when handling chemicals and other hazards, or while working on contaminated surfaces. Chemical gloves can protect employees when handling chemicals and other hazards, or while working on contaminated surfaces. Chemical-resistant gloves may be made from natural rubber, neoprene, nitrile, PVC, polyethylene, or other substances to protect against hazardous chemicals.
Body Protection: Aprons, coats, gowns, and full-body suits-sometimes coated in polyethylene for added protection-may be made from rubber, leather, or synthetics. Effective body protection blocks hazards posed by particles, aerosols, and chemicals that may splash onto an employee.
Respiratory Protection: Respirators are essential to keep from breathing air contaminated with gases, vapors, fumes, sprays, dusts, fogs, mists, or smoke. Respirators may cover the nose and mouth, a worker's entire face, or the entire head. All respirators must be approved by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
Note: An employer must provide a medical evaluation and training before an employee may use a respirator, and all employees should ensure their respirator fits properly, seals out hazardous air, and that it's properly cleaned, stored, and maintained.
Eye and Face Protection: Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields can protect against splashes. All eyewear should be compliant with the ANSI Z87.1 and CSA Z94.3 standards, which set the criteria for testing, selecting, maintaining, and using of eye protection in American and Canadian workplaces, respectively.
DuraLabel Resources for Chemical Hazard PPE Programs
Managing chemical risks requires more than providing equipment. Clear visual communication helps employees understand when chemical hazard PPE is required, which protection to use, and where hazards exist. Labels and signs reinforce training and support safer decision-making at the point of use.
DuraLabel Industrial Sign and Label Systems allow facilities to create durable, OSHA-aligned signage that supports hazard assessment findings and PPE requirements. From labeling chemical storage areas to posting reminders for chemical gloves, eye protection, and respirators, in-house printing helps keep safety communication current as hazards change.
For teams building or updating chemical safety programs, DuraLabel’s free HazCom Labeling Quick Start Guide is a practical resource. It breaks down OSHA HazCom requirements, explains how chemical labels and safety data sheets support PPE selection, and provides real-world examples for labeling hazardous materials.
Have questions about PPE signage, chemical labeling, or selecting the right materials for harsh environments? Call 1-888-789-7964 to speak with a DuraLabel safety and compliance specialist.
Read Next:
Related Resources

Chemical Hazards in the Workplace Overview
What Are Hazardous Chemicals? Hazardous chemicals, often identified by DOT hazardous material labels during ...
Read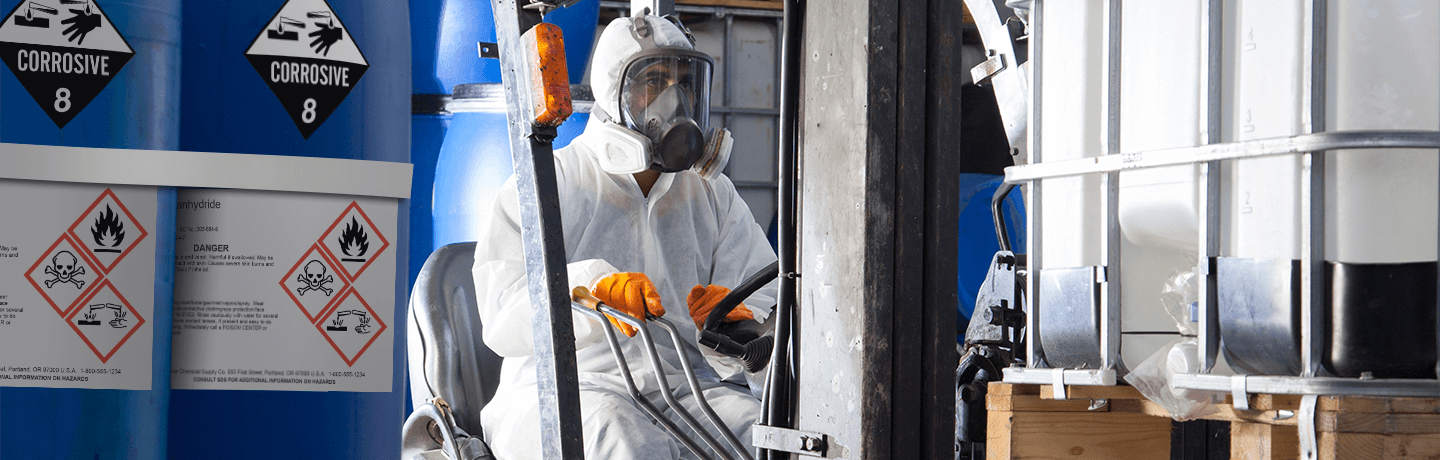
HMIS Labeling and How the HMIS Labeling System Works
How Does the HMIS Labeling System Work? The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS)uses color bars ...
Read
OSHA Rules for Chemical Hazards
What Are OSHA Rules for Hazardous Chemicals? OSHA rules for hazardous chemicals focus on identifying chemical ...
Read.png)





