ELECTRICAL SAFETY
What is the cost of compromised electrical safety?
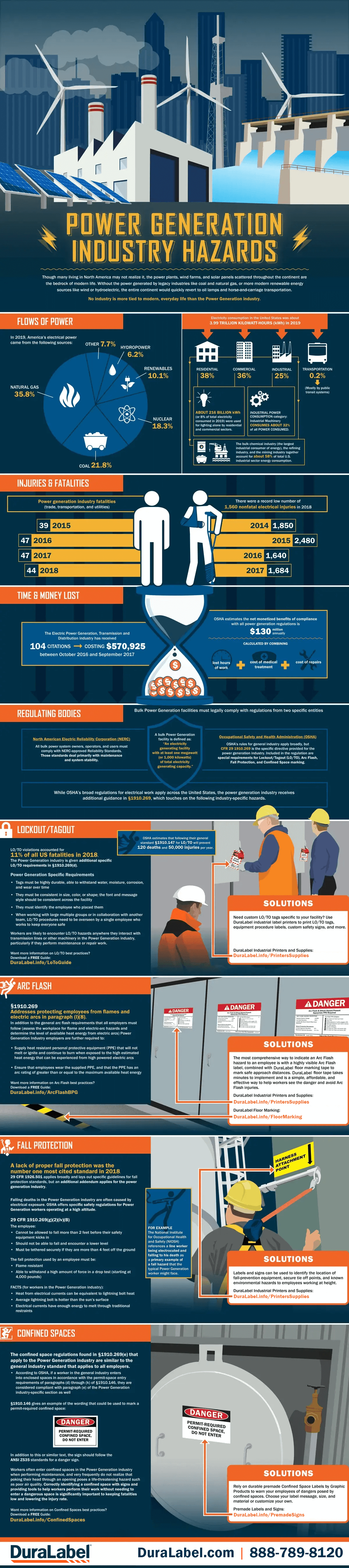
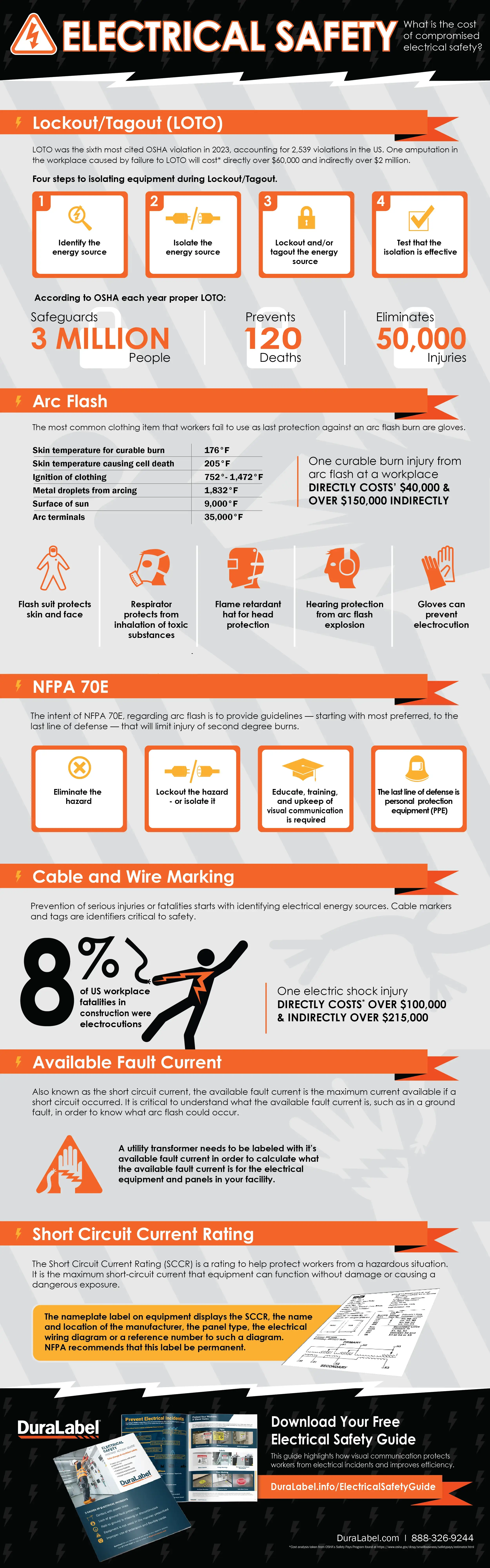
Infographic Transcription
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
LOTO was the sixth most cited OSHA violation in 2023, accounting for 2,539 violations in the US. One amputation in the workplace caused by failure to LOTO will cost* directly over $60,000 and indirectly over $2 million.
Four steps to isolating equipment during Lockout/Tagout.
- Identify the energy source
- Isolate the energy source
- Lockout and/or tagout the energy source
- Test that the isolation is effective
According to OSHA each year proper LOTO:
Safeguards 3 MILLION People
Prevents 120 Deaths
Eliminates 50,000 Injuries
Arc Flash
The most common clothing item that workers fail to use as last protection against an arc flash burn are gloves.
Skin temperature for curable burn — 176°F
Skin temperature causing cell death — 205°F
Ignition of clothing — 752° - 1,472°F
Metal droplets from arcing — 1,832°F
Surface of sun — 9,000°F
Arc terminals — 35,000°F
One curable burn injury from arc flash at a workplace DIRECTLY COSTS* $40,000 & OVER $150,000 INDIRECTLY
Flash suit protects skin and face
Respirator protects from inhalation of toxic substances
Flame retardant hat for head protection
Hearing protection from arc flash explosion
Gloves can prevent electrocution
NFPA 70E
The intent of NFPA 70E, regarding arc flash is to provide guidelines — starting with most preferred, to the last line of defense — that will limit injury of second degree burns.
Eliminate the hazard
Lockout the hazard - or isolate it
Educate, training, and upkeep of visual communication is required
The last line of defense is personal protection equipment (PPE)
Cable and Wire Marking
Prevention of serious injuries or fatalities starts with identifying electrical energy sources. Cable markers and tags are identifiers critical to safety.
8% of US workplace fatalities in construction were electrocutions
One electric shock injury DIRECTLY COSTS* OVER $100,000 & INDIRECTLY OVER $215,000
Available Fault Current
Also known as the short circuit current, the available fault current is the maximum current available if a short circuit occurred. It is critical to understand what the available fault current is, such as in a ground fault, in order to know what arc flash could occur.
A utility transformer needs to be labeled with it's available fault current in order to calculate what the available fault current is for the electrical equipment and panels in your facility.
Short Circuit Current Rating
The Short Circuit Current Rating (SCCR) is a rating to help protect workers from a hazardous situation. It is the maximum short-circuit current that equipment can function without damage or causing a dangerous exposure.
The nameplate label on equipment displays the SCCR, the name and location of the manufacturer, the panel type, the electrical wiring diagram or a reference number to such a diagram. NFPA recommends that this label be permanent.
DuraLabel
Download Your Free Electrical Safety Guide
This guide highlights how visual communication protects workers from electrical incidents and improves efficiency.
DuraLabel.info/ElectricalSafetyGuide
DuraLabel.com | 888-326-9244
.png)
.webp)