Miswired and Mislabeled: The Electrical Errors That Could Cost You
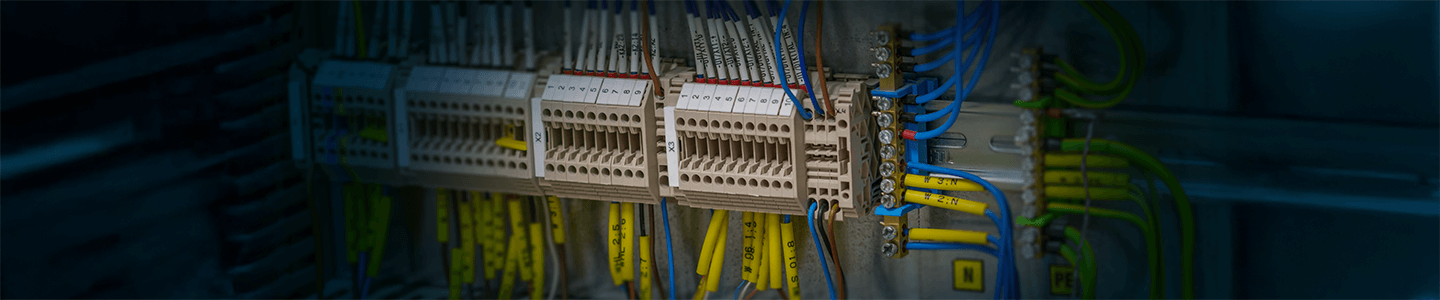
Electrical failures and malfunctions remain a major safety concern, causing injuries, fatalities, and significant property damage each year. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), fire departments responded to an estimated average of 46,700 home fires involving electrical failure or malfunction annually between 2015 and 2019. These incidents resulted in approximately 390 civilian deaths, 1,330 civilian injuries, and $1.5 billion in direct property damage each year.
Electricians and related industry professionals face considerable occupational hazards. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported that in 2020, electrical power-line installers and repairers experienced 26 fatal work injuries. Additionally, there were:
- 26 workplace fatalities among electrical power-line installers and repairers
- 2,220 nonfatal injuries involving days away from work
- 17% increase in nonfatal workplace injuries over 2019
Understanding these industry trends highlights the importance of following best practices in electrical wiring and labeling to enhance safety, ensure compliance, and improve long-term system reliability.
How to Prevent Miswiring
Miswiring can cause circuit malfunctions, electrical shocks, and fires. The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets clear guidelines for wiring practices, including wire gauge requirements to prevent overheating and fire hazards. For instance, 15-amp circuits require 14-gauge wire, while 20-amp circuits require 12-gauge wire. Following these standards helps prevent overheating and circuit failure.
The ANSI/TIA-606-B standard establishes a structured framework for labeling electrical systems, improving maintenance and troubleshooting efficiency. Effective labeling should specify circuits, voltage levels, and functions to simplify future inspections and repairs.
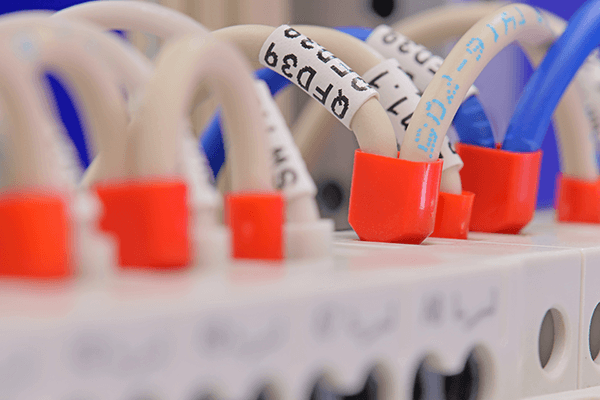
To avoid miswiring, consider the following best practices:
- Verify connections before energizing the system: Always double-check that all wires are properly connected before turning on power. Mistakes at this stage can lead to short circuits or equipment damage.
- Use circuit testers: These devices help ensure conductors are correctly positioned, preventing issues like reversed polarity or disconnected wires.
- Label wires accurately: Clear identification of each wire's function reduces confusion and simplifies future maintenance. ANSI/TIA-606-B provides a structured approach to labeling, helping to keep track of circuits in an organized manner.
- Follow standardized color codes: Using NEC-approved color-coding makes it easier to distinguish between hot, neutral, and ground conductors, reducing the risk of miswiring.
- Conduct a final inspection: Once wiring is complete, perform a thorough check against design schematics and test the system to confirm everything functions as expected.
To avoid miswiring, consider the following best practices:
- Verify connections before energizing the system: Always double-check that all wires are properly connected before turning on power. Mistakes at this stage can lead to short circuits or equipment damage.
- Use circuit testers: These devices help ensure conductors are correctly positioned, preventing issues like reversed polarity or disconnected wires.
- Label wires accurately: Clear identification of each wire's function reduces confusion and simplifies future maintenance. ANSI/TIA-606-B provides a structured approach to labeling, helping to keep track of circuits in an organized manner.
- Follow standardized color codes: Using NEC-approved color-coding makes it easier to distinguish between hot, neutral, and ground conductors, reducing the risk of miswiring.
- Conduct a final inspection: Once wiring is complete, perform a thorough check against design schematics and test the system to confirm everything functions as expected.
Standardizing wire color codes, as recommended by the NEC, makes it easier to distinguish neutral, hot, and ground conductors, reducing the risk of miswiring. A post-installation inspection ensures that all connections match the circuit design, minimizing the risk of errors and corrections down the line.
Ensuring Effective Grounding
Grounding creates a safe path for electrical currents, reducing the risk of electric shock and equipment damage. The NEC mandates the installation of ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) in areas exposed to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor locations. Regular inspections of ground connections ensure low-resistance paths remain intact, preventing failures caused by corrosion.
To establish a reliable grounding system, follow these steps:
- Install NEC-compliant ground rods or loops: These components direct excess electrical energy into the ground, preventing hazardous voltage buildup.
- Perform regular ground resistance testing: This detects corrosion or degradation over time, ensuring the system functions properly.
- Bond all metal components: Connecting metal enclosures, conduit systems, and grounding conductors prevents stray voltage and improves system stability.
- Incorporate surge protection devices (SPDs): When combined with grounding, SPDs prevent transient voltage spikes from damaging sensitive equipment, particularly in facilities with heavy electrical loads.
Following these best practices ensures a grounding system that enhances electrical safety and system reliability.
How to Prevent Breaker Overloads
Breaker overloads happen when circuits exceed their rated capacity, causing tripped breakers and potential fire hazards. The NEC provides specific guidelines on breaker sizing and load distribution to prevent these issues.
Take these precautions to avoid overloads:
- Conduct an energy audit: An energy audit assesses electricity distribution across a facility, identifying circuits near capacity and ensuring efficient power allocation. This helps distribute loads more efficiently and prevents sudden breaker trips. An audit should be conducted annually, and in high-demand environments, semi-annually.
- Monitor load levels with smart panels: Modern electrical panels provide real-time data on power usage and circuit loads. These panels detect imbalances early, allowing adjustments before an overload occurs, which improves energy efficiency and system reliability.
- Install dedicated circuits for high-power appliances: Appliances like HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and commercial kitchen equipment require significant power. Dedicated circuits for these loads prevent voltage fluctuations and keep other areas stable.
- Label breaker panels clearly: Marking circuits accurately helps electricians quickly identify power sources, reducing the likelihood of overloading or miswiring.
- Regularly test breaker function: Schedule annual inspections to ensure breakers operate correctly and replace any that show signs of wear or malfunction.
Clear breaker labeling improves safety and efficiency. Well-marked panels help electricians quickly identify circuit assignments, reducing the risk of mismanaged load distribution. OSHA 1910.335(b)(1) highlights the need for high-visibility labeling to keep essential circuit information readily accessible.
Adhere to Labeling Standards
Standardizing electrical labeling is essential for efficient maintenance, regulatory compliance, and quick emergency troubleshooting. A clear labeling system simplifies circuit identification, reducing time spent troubleshooting and minimizing errors. Underwriters Laboratories (UL) developed UL 969, a widely recognized standard that ensures electrical labels remain legible under harsh conditions.
To improve labeling practices, implement the following steps:
- Use durable labeling material: Labels must withstand heat, moisture, and chemical exposure. Thermal transfer labels and laminated markers comply with ANSI/UL 969 durability standards.
- Implement a color-coded identification system: Using different colors for voltage levels, circuit types, and safety warnings improves clarity and enhances troubleshooting efficiency.
- Regularly update labels: Electrical systems change over time. Ensuring labels reflect modifications and new installations helps prevent confusion and errors during maintenance.
- Maintain updated electrical schematics: Keeping electrical schematics updated and aligned with labeled components simplifies troubleshooting and ensures system consistency.
DuraLabel Electrical Labeling Resources
Avoiding costly electrical mistakes requires careful planning, adherence to industry standards, and clear, durable labeling. Proper identification of circuits, wires, and panels reduces the risk of miswiring, improves maintenance efficiency, and enhances overall safety. For effective labeling, a reliable solution like DuraLabel’s Toro Max Industrial Sign and Label Print System keeps wire markers and equipment labels legible in demanding environments. With high-quality thermal transfer printing, labels withstand heat, moisture, and abrasion, making them a long-lasting option for electrical applications.
For guidance on electrical safety, DuraLabel’s free Electrical Safety Quick Start Guide provides practical steps to improve safety, reduce hazards, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Download your free copy today to proactively address electrical hazards and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Do you have questions about labeling solutions for your electrical system? Our safety professionals are ready to help. Whether you need guidance on compliance, best practices, or selecting the right materials for your facility, we provide expert support tailored to your needs. Call us today at 1-888-820-4631 and take the first step toward a more organized and compliant electrical system.
Read Next:
Related Resources

Why Custom Industrial Labels Matter for Mechanical Job Sites
Mechanical job sites are fast-paced environments where precision and organization are critical. Mislabeling ...
Read
The Key to Reliable Construction Projects: Safety Signage That Works
Construction signs and labels play a crucial role in protecting workers and keeping projects on schedule. ...
Read
8 Essential HVAC Installation Tips to Prevent Costly Mistakes
HVAC Installation Done Right: 8 Essential Tips to Prevent Costly Mistakes A poorly installed heating, ...
Read.png)





