Quick Response Codes and Kanban

Quick Response codes, commonly known as QR codes, are two-dimensional barcodes that can be scanned and interpreted by mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. While QR codes are often seen on consumer products and in advertising they originated as a solution to improve part tracking in a manufacturing context. This article explores the use of QR codes to help improve the dissemination of safety and other key information by integrating them onto the cards of a physical Kanban board and the durable labels affixed to the work-in-process (WIP) of the production flow.
How are Quick Response Codes Used by Lean Manufacturing?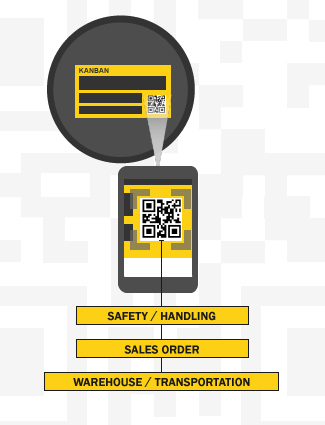
The purpose of a QR code is to quickly and reliably provide information in a physical context ? that is, the information is associated with a place or object, where the code appears. The device that scans the code can then act on that information.
QR codes provide up to 4,296 characters of alphanumeric data (or 7,089 characters of numeric-only data), which makes it feasible to encode a significant amount of information into a Kanban card and WIP label. The device might simply record the information for later use, display it in readable form to a user, or even follow instructions to perform an action. This can help track the movement of materials through your production processes, such as an order number and product specifications, or a part description and serial number. It could even offer written instructions for an employee to follow when the code appears.
QR codes can be placed on anything. The main criteria are that they be large enough that the device can accurately scan them. Typically, a one-inch square is easily readable. However, QR codes may need to be larger when printed on a label for uneven surfaces, such as fabric, or when being scanned from a distance.
For a lean manufacturing facility that uses Kanban, QR codes are ideal for embedding critical information, including:
- Safety and handling information-such as a link to a safety data sheet (SDS)
- Sales order information- including the destination, lead time, and priority
- Warehouse and transportation- route information
Most frequently, the mobile device that scans a QR code will open a website ? but the device may also make a phone call, post information back to the enterprise resource planning (ERP) or scheduling status system, display the destination of a scanned WIP assembly, or send an automated message to another department. The usefulness of a QR code is only limited by the programming of the device that scans it.
QR codes help disseminate safety and other key information by integrating them onto the cards of a physical Kanban board and the durable labels affixed to the work-in-process (WIP) of the production flow. This approach retains the benefits of the visual Kanban system while adding embedded information that is crucial to the safety and efficiency of the production system. In this scenario, information for a QR code for each production batch or customer order is exported from the ERP database. That data is then encoded into a QR code image by custom label design software. An industrial label printer that supports both paper and vinyl labels print the Kanban cards and the durable labels affixed to WIP.
Synchronized Physical and Digital Kanban Boards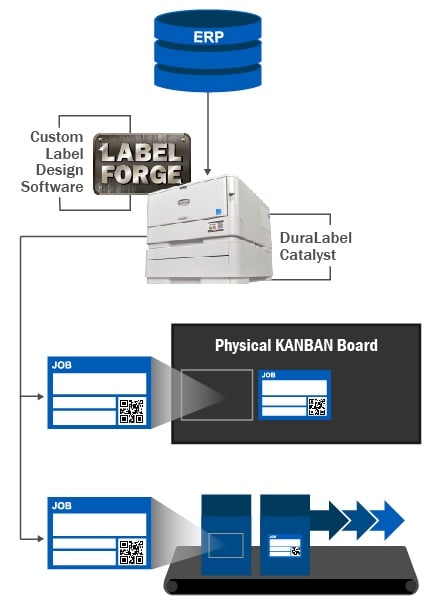
An important characteristic of Kanban is that it is visual. For example, anyone in the production area can glance at the Kanban board and know the overall status of production. Physical Kanban boards encourage communication and collaboration by the production staff and provide a reminder of goals and achievements, but they can be difficult to manage, record, and share outside the immediate area. Switching to a digital Kanban system, while providing many data collection and sharing advantages, is still constrained by what is traditionally written on each card. What is needed is a way to embed more information while retaining a convenient size for handling. That can be accomplished using QR codes. In a hybrid Kanban board system, the physical Kanban board is linked to the digital Kanban board by photographing it each time a card is added or moved on the board. In this way, both the physical and digital Kanban boards can be scanned from the production floor or anyone viewing the digital version to access the embedded information.
QR Code and Kanban Resources
A Kanban system that includes cards and labels with QR codes requires a convenient way to import and encode information and then print cards and durable labels that will withstand the conditions of the production floor. LabelForge Labeling Software supports a variety of common formats to import data and encode it into QR codes for a card/label design. DuraLabel industrial label and sign printers pair with high-performance DuraLabel supplies to create a card/label print station that provides the flexibility to support both production planning and WIP labeling.
For more information on Kanban and how it can help create a lean work process, check out Duralabel Best Practice Guide to Kanban. Duralabel can help develop a Kanban system best suited your workplace.
Related Resources
Heijunka Box for Lean Production Leveling
What Is a Heijunka Box and How Does It Support Lean Production? TheHeijunka boxis a scheduling tool used ...
Read
House of Lean: Building the Lean Manufacturing Framework
What Is the House of Lean? The House of Lean is a useful tool that can help you understand Lean Manufacturing ...
Read
Lean Logistics Techniques
What Are Lean Logistics Techniques? Lean logistics techniqueshelp organizations streamline supply chain ...
Read.png)





