Workplace Chemical Labels and GHS Requirements Explained

What is Chemical Labeling?
Clear chemical labels help workers recognize hazards quickly, select the right PPE, and respond correctly during spills, exposure incidents, or fires. They also support consistent training and safer chemical storage across departments and job sites.
For employers, chemical labeling is not just a best practice. It is a compliance requirement tied to hazard classification, Safety Data Sheets (SDS), and workplace communication procedures.
In this article, you’ll learn:
-
What chemical labeling is and why it matters for safety and compliance
-
How GHS chemical labeling requirements apply under OSHA HazCom
-
Which information must appear on workplace chemical labels
-
Which containers must be labeled in the workplace
-
How Safety Data Sheets (SDS) support chemical labeling programs
-
Common chemical labeling mistakes and how to avoid them
-
Best practices for maintaining labels in harsh industrial environments
Now that you know what chemical labeling is, the next step is understanding the compliance framework behind it. The section below explains how OSHA HazCom and GHS work together and what that means for required label information in the workplace.
The Compliance Landscape: GHS and HazCom
GHS is a worldwide initiative aimed at standardizing chemical hazard communication. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) applies GHS principles through HazCom, which establishes baseline GHS chemical labeling requirements for how chemical hazards are classified and communicated.
Hazardous chemicals can range from household cleaners to lethal gases, and their health effects can vary from mild skin irritation to severe outcomes such as cancer or organ damage. These chemicals show up in nearly every industry, including manufacturing, healthcare, and construction.
To use workplace chemical labels correctly, workers need to understand what qualifies as a hazardous chemical under HazCom and how to handle substances safely based on the hazards identified.
What Defines a Hazardous Chemical?
OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard 29 CFR 1910.1200 defines what qualifies as a hazardous chemical. In 2012, OSHA aligned HazCom with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS), and OSHA has since issued updates and corrections to clarify parts of the rule text and appendices. These are defined as:
"Any chemical which is classified as a physical hazard and include fire hazards, explosion hazards, and reactive hazards."
 These hazards are generally broken down into two main categories: physical hazards and health hazards. The "physical hazard" and "health hazard" categories are included in the GHS. The other hazard types listed in that definition were added by OSHA, to fill the gaps in the international standard.
These hazards are generally broken down into two main categories: physical hazards and health hazards. The "physical hazard" and "health hazard" categories are included in the GHS. The other hazard types listed in that definition were added by OSHA, to fill the gaps in the international standard.
Physical hazards include fire hazards (including combustible liquids and flammable materials), explosion hazards (including compressed gas and explosives), chemical under pressure, and reactive hazards (including organic peroxide and unstable materials).
Health hazards fall into two categories: systemic effects (including carcinogens, corrosive materials, and irritants) and target organ effects (including neurotoxins and respiratory toxins). In order to pose a health hazard, significant evidence (such as at least one study) must indicate that exposure may have acute or chronic health effects.
The severity of these hazardous chemicals is reflected in a numbered category. Category 1 contains the most severe hazards (such as propane, a flammable gas), and the category numbers increase as the severity of each hazard decreases. Different hazard classes have different numbers of categories.
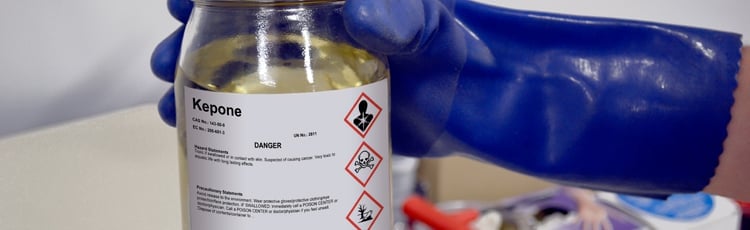
These hazards, ingredient information, and more details about a given chemical are communicated on a Safety Data Sheet (SDS), required in the HazCom 2012 standard. Some of those details are also required to appear on industrial safety labels placed on the chemical's container.
OSHA has also issued an advisory guide for hazard determination to help employers understand and comply with HazCom 2012 regulations. The guide assists employers with determining hazards, selecting chemicals, and analyzing data.
Dangerous Chemical Consequences
It's vital to wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE) while working around hazardous chemicals. OSHA's general PPE requirements for most workplaces can be found in 29 CFR 1910.132. Employees who don't comply with these regulations may face severe consequences when working with dangerous chemicals.
- Skin irritation: If employees aren't wearing the appropriate PPE and come in contact with hazardous materials, they may experience rashes, burns, skin irritation, and more.
- Respiratory damage: When employees work in areas that lack proper ventilation or don't wear respirators, they may be exposed to fumes from hazardous chemicals. This can result in immediate illness or even death, and in the long term, may lead to lung cancer or other respiratory illnesses.
- Burns: Workers may be severely burned when they don't wear proper PPE. Explosive chemicals may trigger blasts in a facility, and flammable chemicals may catch fire if not properly handled or stored.
Clear hazard identification helps prevent these outcomes before work begins. Workplace chemical labels and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) give employees the information they need to recognize hazards quickly and follow safe handling procedures.
Key GHS Chemical Labeling Requirements:
- Permanent Container Safety Labels: These labels must withstand various environmental conditions, maintaining legibility and adhesion.
- Secondary Container Industry Safety Labels: Often transferred to smaller containers, these lab labels require the same level of detail and durability as primary hazard communication labels.
- Replacement Container Safety Labels: In the event of label damage or deterioration, replacements must be immediately available and compliant.
- Lab Safety Label Regulations: A medical lab must adhere to stringent labeling practices to prevent accidents and ensure quick identification of hazardous substances.
GHS Compliance Challenges in Medical Facilities
- Diverse Chemical Usage: A medical office and lab uses a broad range of chemicals, each requiring specific handling and HazCom labeling.
- Dynamic Environments: Constant movement of materials and personnel increases the risk of label damage and misplacement.
- Education and Training: Ensuring all staff are adequately trained on GHS and HazCom standards can be resource-intensive.
- Regulatory Updates: Staying current with evolving regulations necessitates continuous monitoring and adaptability.
Working with Hazardous Chemicals
Employers and employees should do all they can to prevent catastrophic events around dangerous chemicals. This can be done through a combination of education, proper PPE, and signage that alerts workers to nearby hazards.
Proper PPE is often necessary when working around dangerous chemicals. You may need to protect your workers from head to toe with protective gear, including respiratory protection, as well as protection for the hands, feet, face, and more. Let employees know when PPE is required with clear warning labels and signs.
Employers should be up-to-date and in compliance with OSHA's HazCom 2012 regulations. The rules help employees understand the hazards posed by the chemicals they work with, including handling and storage guidelines, firefighting measures, exposure controls, and more. Request DuraLabel’s free Best Practice Guide to HazCom 2012 Labeling for detailed information.
Visual Communication HazCom Solutions
Effective visual communication is crucial in overcoming these compliance challenges. The following solutions can enhance HazCom labeling practices in medical facilities:
- Durable HazCom Label Materials: Utilizing high-quality, durable materials for HazCom labels ensures they remain intact and legible under various conditions. Laminated or UV-coated industrial safety labels can resist chemicals, moisture, and abrasion.
- Clear and Consistent Icons: Standardized GHS pictograms and icons provide immediate hazard recognition, reducing the risk of mishandling. Incorporating color coding can further enhance visibility and comprehension.
- Integrated GHS Labeling System: Adopting electronic labeling systems that generate and print compliant lab labels on demand can streamline the HazCom labeling process. These systems can be integrated with inventory management software to ensure accurate and up-to-date information.
- Customizable Templates: Offering customizable label templates that align with GHS and HazCom standards allows for easy adaptation to specific needs. This flexibility ensures HazCom labels meet all regulatory requirements while accommodating facility-specific nuances.
- Training and Resources: Providing comprehensive training programs and readily accessible resources on GHS and HazCom standards is essential. Visual aids, such as instructional videos and interactive modules, can enhance understanding and retention.
- Regular Audits and Inspections: Implementing routine audits and inspections to assess label condition and compliance can proactively identify and address potential issues. Utilizing checklists and mobile inspection tools can streamline this process.
HazCom Solutions from DuraLabel
Navigating the complexities of HazCom labeling compliance in medical facilities requires a strategic approach that emphasizes durability, clarity, and consistency. By leveraging advanced visual communication solutions, healthcare providers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance overall safety and efficiency.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive is key. Embracing innovative HazCom labeling technologies and practices will position medical facilities at the forefront of compliance and safety, ultimately contributing to better patient care and operational excellence.
Custom chemical hazard labels such as those made by DuraLabel industrial sign and label print systems can help you develop effective visual communication. DuraLabel carries more than 50 specialty supplies suited to application and industry-specific uses. Download our free Safety Data Sheets Guide for a comprehensive resource.
Read Next:
Ensuring Lab Safety with Proper Labeling
GHS-HazCom for Medical Facilities
Related Resources
Hazard Control Hierarchy and Lab Safety Labels for Chemical Hazards
What Are Lab Safety Labels? Lab safety labels are visual identifiers that communicate chemical and process ...
Read
Why a GHS Labeling System Matters for Hazard Communication
What Is GHS Labeling? GHS labeling is a standardized method for communicating chemical hazards in the ...
Read
Hazardous Chemical Storage Risks and GHS Labeling Solutions
How Do Labels Support Safe Chemical Storage? Labels support safe storage of hazardous materials by clearly ...
Read.png)