HMIS Labeling and How the HMIS Labeling System Works

Worker in full chemical PPE operating equipment beside drums with corrosive and GHS hazard labels, illustrating HMIS hazardous materials identification labeling for safe handling and compliance.
How Does the HMIS Labeling System Work?
The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) uses color bars and numbers to rate health, flammability, and physical hazards, with a separate field for recommended personal protective equipment. As an HMIS hazardous materials identification system, it helps workers quickly interpret HMIS standards and HazCom risk levels and apply safer handling practices. HMIS labels are often used alongside SDS information and workplace training.
The sections below explain how HMIS labeling is structured, what each color and number means, and how to apply the HMIS labeling system consistently in a facility:
-
What the color bars mean and how the 0 to 4 ratings work
-
How PPE codes are assigned and used
-
How HMIS labeling compares with other hazard rating systems
-
Common mistakes that reduce label clarity
Next, we will break down the HMIS label layout and what each color bar communicates.
HMIS Labeling and OSHA Signs for Hazardous Environments
In hazardous environments, understanding the HMIS labeling system and OSHA signs is crucial for ensuring safety. The HMIS labeling system was developed by National Paint Coatings Association (NPCA), now known as the American Coatings Association (ACA), employs color bar labels to signify and convey information about chemical hazards. Complementing HMIS, OSHA signs play a pivotal role in alerting individuals to potential dangers and safety protocols within workplaces. Let's delve into these systems to better grasp their significance in safeguarding workers and environments.
The Hazardous Materials Identification System (HMIS) is a hazard rating system that uses color bar labels to identify and provide information about chemical hazards. HMIS was developed by the National Paint Coatings Association (NPCA), now known as the American Coatings Association (ACA).
HMIS labels are similar to NFPA diamond RTK labels, and many workplaces use the same rating systems for both.
In addition to official HMIS labels, other color bar style RTK labels are available through suppliers such as DuraLabel. Although not officially HMIS labels, DuraLabel color bar labels communicate the same information as HMIS labels and meet OSHA labeling requirements.
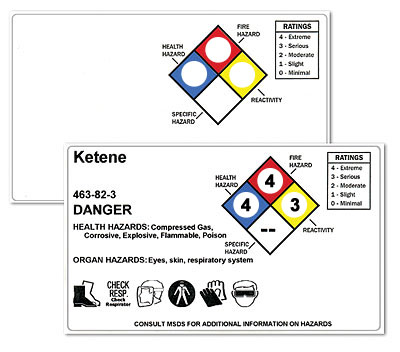
Hazardous chemical container label example featuring an NFPA 704 diamond.
Comparing NFPA Diamond and the HMIS Labeling System
NFPA diamond labels, HMIS labels, and color bar RTK labels provide the same information, but in different ways. The most significant example of their differences is the NFPA diamond, which is used to rate the instability (or reactivity) of the material. The yellow diamond has been replaced with an orange bar to rate the level of the physical hazard on the HMIS label, and is also used in the same way to create RTK labels. Used correctly, HMIS labeling and NFPA diamonds support hazard communication by giving workers a quick way to interpret risk levels. OSHA signs can reinforce these ratings by directing attention to required precautions and safe work practices.
HMIS Labeling Blue Bar: Health Hazards
For blue, the NFPA and HMIS rating systems are the same. The health section of an HMIS labeling system conveys the health hazards of the material.
![]() This material presents no health hazard. No precautions are needed.
This material presents no health hazard. No precautions are needed.
![]() Exposure to the material will cause an irritation and result in minor residual injuries.
Exposure to the material will cause an irritation and result in minor residual injuries.
![]() Material may be harmful if inhaled or absorbed. Intense or continued exposure might cause temporary incapacitation. There may be a residual injury even with treatment.
Material may be harmful if inhaled or absorbed. Intense or continued exposure might cause temporary incapacitation. There may be a residual injury even with treatment.
![]() These materials are corrosive or toxic. Avoid skin contact or inhalation. Short exposure may cause serious temporary or moderate residual injury even with prompt medical treatment.
These materials are corrosive or toxic. Avoid skin contact or inhalation. Short exposure may cause serious temporary or moderate residual injury even with prompt medical treatment.
![]() Personal protective gear (PPE) is required These chemicals can penetrate ordinary rubber protective gear. Short exposure may result in death.
Personal protective gear (PPE) is required These chemicals can penetrate ordinary rubber protective gear. Short exposure may result in death.
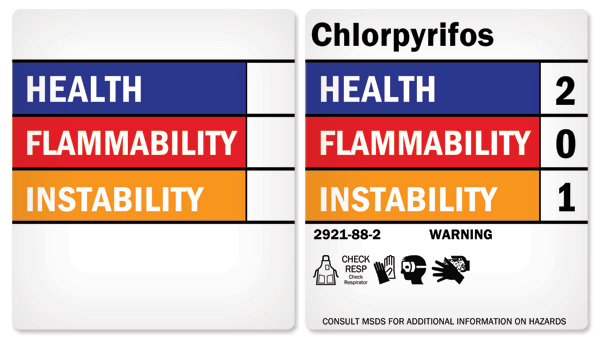
HMIS label example showing color-bar hazard ratings for hazardous materials identification and safety compliance labeling.
In addition to the numerical rating, the HMIS allows for an asterisk to be used in a separate box in the blue bar to indicate that long-term exposure may cause health problems.
HMIS Labeling System Red Bar: Flammability
There are three HMIS standards that have been issued by NPCA. For the HMIS I and II standards, the criteria for the numerical values in the red bar are the same as for the NFPA diamond. For HMIS III the criteria are the OSHA label standards.
Here are the two standards:
![]() Not combustible. The material will not burn in air when exposed to a temperature of 1,500 (F) for five minutes.
Not combustible. The material will not burn in air when exposed to a temperature of 1,500 (F) for five minutes.
![]() Combustible when exposed to a temperature of 1,500 (F) for less than five minutes or with a flash point above 200 (F).
Combustible when exposed to a temperature of 1,500 (F) for less than five minutes or with a flash point above 200 (F).
![]() Under normal ambient conditions, this material does not form a hazardous atmosphere. Under high ambient temperatures or moderate heating, it will produce a hazardous atmosphere. These substances may be solids that readily give off hazardous gases or liquids with a flash point above 100 (F) and below 200 (F).
Under normal ambient conditions, this material does not form a hazardous atmosphere. Under high ambient temperatures or moderate heating, it will produce a hazardous atmosphere. These substances may be solids that readily give off hazardous gases or liquids with a flash point above 100 (F) and below 200 (F).
![]() These are solids and liquids that can be ignited under ambient conditions. Liquids with this rating have a flash point below 100 (F). This rating also includes combustible dusts, fibrous solids and materials that have self-contained oxygen.
These are solids and liquids that can be ignited under ambient conditions. Liquids with this rating have a flash point below 100 (F). This rating also includes combustible dusts, fibrous solids and materials that have self-contained oxygen.
![]() Flammable gas or extremely flammable liquids. Materials that form explosive mixtures with air.
Flammable gas or extremely flammable liquids. Materials that form explosive mixtures with air.
HMIS III Criteria in the HMIS Labeling System
![]() Material that will not burn
Material that will not burn
![]() Materials that have a flash point above 200F
Materials that have a flash point above 200F
![]() Materials that have a flash point at or above 100 F (38 C) but below 200 F (93 C)
Materials that have a flash point at or above 100 F (38 C) but below 200 F (93 C)
![]() OSHA Class IB materials which are liquids having flashpoints below 73 F (22.8 C) and having a boiling point at or above 100 F (37.8 C)
OSHA Class IB materials which are liquids having flashpoints below 73 F (22.8 C) and having a boiling point at or above 100 F (37.8 C)
![]() OSHA Class IA materials include liquids having flashpoints below 73 F (22.8 C) and having a boiling point below 100 F (37.8 C)
OSHA Class IA materials include liquids having flashpoints below 73 F (22.8 C) and having a boiling point below 100 F (37.8 C)
HMIS Labeling System Orange Bar: Physical Hazard
The HMIS physical hazard level ratings are:
![]() Materials that do not react with most materials, and pose no physical hazard.
Materials that do not react with most materials, and pose no physical hazard.
![]() Materials that are stable at normal temperatures and pressures, but may become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures.
Materials that are stable at normal temperatures and pressures, but may become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures.
![]() Materials that may have violent reactions at normal temperatures and pressures.
Materials that may have violent reactions at normal temperatures and pressures.
![]() Materials that may create explosive mixtures at normal temperatures and pressures.
Materials that may create explosive mixtures at normal temperatures and pressures.
![]() Materials that may explode at normal temperatures and pressures.
Materials that may explode at normal temperatures and pressures.
HMIS Labeling System White Bar: Personal Protection Equipment Requirements
In the HMIS hazardous materials identification system, the white bar is used to show the level of personal protective equipment that needs to be used. An alphabetical system is used, with letters indicating the level of protection:
![]() safety glasses
safety glasses
![]() safety glasses and gloves
safety glasses and gloves
![]() safety glasses, gloves, and an apron
safety glasses, gloves, and an apron
![]() face shield, gloves, and an apron
face shield, gloves, and an apron
![]() safety glasses, gloves, and a dust respirator
safety glasses, gloves, and a dust respirator
![]() safety glasses, gloves, apron, and a dust respirator
safety glasses, gloves, apron, and a dust respirator
![]() safety glasses, a vapor respirator
safety glasses, a vapor respirator
![]() splash goggles, gloves, apron and a vapor respirator
splash goggles, gloves, apron and a vapor respirator
![]() safety glasses, gloves, and a dust/vapor respirator
safety glasses, gloves, and a dust/vapor respirator
![]() splash goggles, gloves, apron, and a dust/vapor respirator
splash goggles, gloves, apron, and a dust/vapor respirator
![]() - hood or mask, gloves, full suit and boots
- hood or mask, gloves, full suit and boots
![]() custom PPE specified by the employer
custom PPE specified by the employer
While HMIS labels are propriety to the NPCA (ACA) and are only available through a single source, Color Bar labels are available in a wide range of sizes. With the DuraLabel Kodiak Max Industrial Sign and Label Print System, you can access RTK labels in various sizes, including unique extra-large label sizes that aren't available from any other label supplier and meet OSHA labeling requirements. The Kodiak Max also comes with RTK database software that makes tracking and printing GHS compliant labels quick and easy.
Whether you need safety signs, pipe markers, or equipment labels—DuraLabel's industrial printers are ready to transport anywhere you are. Get help crafting a system that will provide the safety communication you need. Call 1-888-788-9386 and one of our experts will guide you through the process.
Learn more about establishing and reinforcing industry best practices. Download our free HazCom Instant Action Guide.
Related Resources

Why a GHS Labeling System Matters for Hazard Communication
What Is GHS Labeling? GHS labeling is a standardized method for communicating chemical hazards in the ...
Read
What GHS Chemical Labels Mean for Ammonia System Safety
What Are Common Ammonia Hazards? Ammonia is a highly hazardous chemical commonly used in refrigeration and ...
Read
When Facilities Should Upgrade an Industrial Label Printer
When Should You Upgrade Your Industrial Label Printer? Facilities should upgrade an industrial label printer ...
Read.png)





