What New HVAC Codes Means for A2L Refrigerant Regulations

What Are A2L Refrigerants?
A2L refrigerants are a class of chemicals defined by ASHRAE Standard 34 as having low toxicity and mild flammability. HVAC professionals often ask what does A2L stand for—the term refers to the refrigerant safety classification that identifies low-toxicity, mildly flammable substances. Examples include R-32, R-454B, and R-1234yf. These refrigerants are gaining traction because they offer a significantly lower global warming potential (GWP) compared to older refrigerants like R-410A and R-404A.
Driven by stricter environmental regulations, such as the U.S. American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act and international climate agreements, HVAC manufacturers and contractors are transitioning away from high-GWP refrigerants. A2Ls offer a practical alternative that maintains system performance while reducing environmental impact. This transition also aligns with expanding A2L refrigerant regulations focused on lowering emissions and improving safety across the industry.
This shift reflects the growing alignment of regulatory pressure and market demand for climate-friendly refrigerants. A2Ls are quickly becoming the industry standard for systems to meet modern safety and sustainability goals.
HVAC Codes and A2L Refrigerant Regulations in 2025
Starting in 2025, a series of code updates will reshape how refrigeration systems are designed, labeled, and installed across the United States. Updates to the International Mechanical Code (IMC), International Building Code (IBC), and International Fire Code (IFC) allow wider use of A2L refrigerants. These low-toxicity, mildly flammable compounds with lower GWP are directly affected by new A2L refrigerant requirements introduced to guide safe system installation and operation.
These changes align with updated safety and classification standards issued by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) 15-2024, ASHRAE 34-2024, and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) 60335-2-40. Together, they form a new regulatory framework guiding HVAC systems in design and compliance.
What Does the 2024 ASHRAE Standard Say About A2Ls and A2L Refrigerant Requirements?
The 2024 editions of ASHRAE Standards 15 and 34 introduce updated safety, classification, and installation requirements for refrigerant systems. Standard 15 outlines safety requirements for leak detection, ventilation, and equipment placement when using flammable refrigerants like A2Ls, while Standard 34 defines how refrigerants are categorized by toxicity and flammability.
Together, these standards now serve as the foundation for most U.S. building, mechanical, and fire codes tied to refrigerant systems and related A2L refrigerant regulations.
What’s New in the ASHRAE 2024 Standards:
- A2Ls approved for use in occupied spaces
- New ventilation and minimum room size requirements
- Revised refrigerant charge limits
- Mandatory leak detection for flammable gases
- Additional A2L refrigerants added to the list
- Updated safety group classifications
- Improved flame propagation testing protocols
- Adjusted refrigerant concentration limits for system design
These updates allow building codes to support wider adoption of A2L refrigerants while ensuring systems are safely designed and clearly labeled.
How Do the Standards and A2L Refrigerant Requirements Impact System Design and Compliance?
The latest ASHRAE standards introduce stricter requirements for refrigerant classification, charge limits, ventilation, and labeling, affecting both new construction and retrofit projects. Engineers must now design systems that safely accommodate mildly flammable refrigerants, incorporating A2L refrigerant requirements such as ventilation thresholds, room size considerations, and leak detection placement.
Contractors also need to evaluate how refrigerant group classification affects equipment selection. A system built for a Class A1 refrigerant may not be compatible with an A2L alternative. Before installation, teams must ensure all equipment complies with both ASHRAE and UL/CSA 60335-2-40 standards.
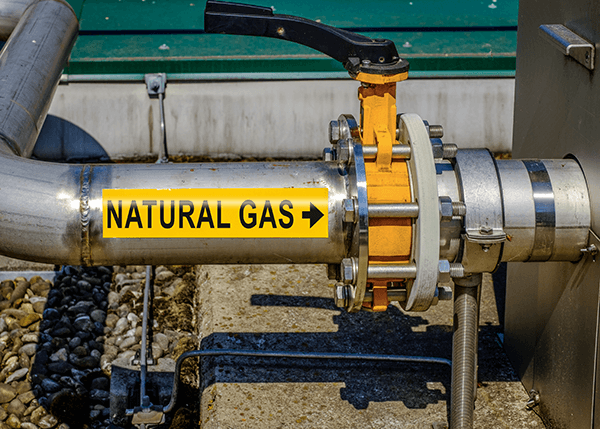
Labeling has also taken on a greater role. Installers must identify the refrigerant type, hazard classification, and related warnings at key points in the system, including piping, compressor units, and access panels. These updates make labeling essential not just for code compliance, but for maintaining worker safety and supporting emergency response efforts.
Why is Accurate Pipe and Component Labeling Critical?
As refrigerant systems evolve, so do labeling requirements. The introduction of new chemical blends and updated safety standards makes it critical for HVAC teams to accurately label every part of a system, especially when working with flammable or toxic refrigerants. Labels must now go beyond identifying contents; they must clearly communicate hazards, pressure states, and compliance with multiple overlapping regulations.
Effective labeling supports code compliance, improves emergency response, and helps ensure safer maintenance procedures. It also bridges the communication gap between system designers, contractors, and facility operators. As systems grow more complex, labeling becomes a frontline defense against costly mistakes.
How Has Ammonia Labeling Changed Under IIAR Appendix Q?

Ammonia remains a core refrigerant in many industrial systems, but its labeling requirements have been updated. The International Institute of Ammonia Refrigeration (IIAR) retired Bulletin No. 114 and replaced it with Appendix Q of Standard 2 to define ammonia system labeling standards. This shift introduces a more detailed, structured labeling format for ammonia piping and components.
Under Appendix Q, ammonia systems must identify these five elements:
- Pressure level (e.g., “HIGH” or “LOW”)
- Physical state (e.g., “LIQ” or “VAP”)
- Pipe contents (always identified as “AMMONIA”)
- Flow direction
- System abbreviation (e.g., HPL for High Pressure Liquid)
Appendix Q emphasizes visibility, consistency, and proper label placement, especially near valves, emergency shutdown zones, and room transitions. Labels must meet specific size and spacing requirements based on pipe diameter and location. Facilities still using outdated labeling practices should review Appendix Q and update their system to remain compliant.
What Are the Labeling Requirements for A2L Refrigerants?
Labeling for A2L refrigerants introduces new considerations. These refrigerants vary in composition and naming, but all share a flammability classification that must be clearly communicated. Many of these expectations overlap with newer A2L refrigerant regulations and safety guidelines.
To remain compliant, systems using A2Ls should:
- Identify the specific refrigerant by name or chemical code
- Display the hazard class
- Include applicable Globally Harmonized System (GHS) pictograms
- Follow OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200)
- Apply ANSI/ASME A13.1 formatting for pipe labeling and color codes
A2Ls are still relatively new to the field, so many facilities use custom label layouts that include fields for pressure, contents, and hazard classification. Technicians apply labels at key locations, such as access points, equipment panels, and any areas with potential refrigerant exposure.
Visible, accurate labeling does more than check a compliance box. It helps teams work safely, reduces confusion, and supports faster response during maintenance or emergencies.
DuraLabel Labeling Resources for A2L Refrigerant Regulations
As refrigerant regulations evolve, HVAC professionals face increasing demands in system design, equipment selection, and safety labeling. The growing use of A2L refrigerants—combined with expanding A2L refrigerant requirements—introduces new obligations for maintaining compliance and protecting workers.
To help teams navigate these requirements, DuraLabel offers a free HVAC Labeling Quick Start Guide, featuring practical insights for labeling ducts, pipes, and panels in accordance with current industry standards. The guide includes material selection advice, placement recommendations, and a reference checklist to help teams implement an efficient and compliant labeling strategy.
For on-site labeling needs, the DuraLabel Toro Max Industrial Sign and Label System provides a portable, all-in-one solution. Equipped with preloaded GHS templates and durable print capabilities, Toro Max empowers field teams to maintain compliance without delays.
Need assistance with other labeling needs? Call us at 1-888-789-7964 and a safety and compliance specialist will guide you through the process.
Read Next:
Top 5 Challenges Mechanical Project Managers Face
8 Essential HVAC Installations Tips to Prevent Costly Mistakes
Related Resources

Ammonia Refrigeration Safety Fundamentals: Pipe Marking and Beyond
Artificial cooling systems keep industry running, and many of these systems use anhydrous ammonia as a ...
Read.png)
8 Essential HVAC Installation Tips to Prevent Costly Mistakes
HVAC Installation Done Right: 8 Essential Tips to Prevent Costly Mistakes A poorly installed heating, ...
Read
Modern HVAC Safety and Efficiency Essentials
The heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration industry is heating up as demand grows, new ...
Read.png)





