What Is An Arc Flash?

An arc flash is an explosive burst of heat and light, caused by a sudden, uncontrolled electrical arc (or current passing through the air). Temperatures may reach as high as 35,000F in just 1/1000 of a second, vaporizing metal, causing fatal burns, and generating a blast wave that can collapse workers' lungs and rupture eardrums. Shrapnel, toxic gases, and intense UV rays can cause additional injuries. Arc flash accidents can kill in an instant, or cause a long, slow, and painful death. Even non-fatal injuries from an arc flash may require months or years of medical care and therapy.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics noted in 2020-2022 that electrical accidents in the workplace caused:
- 70 fatal work injuries
- 7,000 non-fatal injuries
What Happens During an Arc Flash?
An arc can begin whenever a conductive object gets too close to an exposed current source. Here are some examples of how an arc flash can occur:
- Dropping tools
- Opening panels on deteriorated equipment
- Inserting or removing components from an energized system
- Rodent infestation
 If that arc has enough energy, it can continue to ionize the air around it. This ionization reduces the electrical resistance along the path of the arc, allowing the arc to draw even more current. As more and more energy flows through the arc, the process builds on itself, and in a moment the arc becomes an arc flash.
If that arc has enough energy, it can continue to ionize the air around it. This ionization reduces the electrical resistance along the path of the arc, allowing the arc to draw even more current. As more and more energy flows through the arc, the process builds on itself, and in a moment the arc becomes an arc flash.
The primary source of injury in an arc flash is the burst of heat. Similar to lightning, an arc flash releases an enormous amount of heat energy in a very short time. That heat also melts and vaporizes the materials around it, such as wiring and metal equipment panels, as well as drastically raising the temperature of the air nearby.
As this material heats up very quickly, it expands to create a pressure wave, just like thunder. That pressure wave can scatter the broken and melted fragments of equipment like a spray of bullets. Even after the immediate blast, the vaporized material can form a cloud of toxic vapor, mist, and dust. Arc flash is one of the more dramatic electrical accidents, and is often deadly where proper safety precautions have not been taken.
Three Steps for Arc Flash Safety
Preventing arc flash accidents or minimizing their impact requires a comprehensive safety program, involving both electrical workers and management. The following steps should be taken to ensure worker safety. Follow these three steps for arc flash safety:
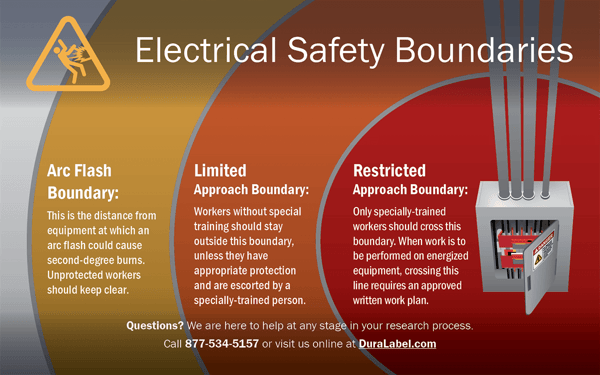
1. Perform an electrical risk assessmentUse the guidelines in NFPA 70E and IEEE 1584 to identify and assess electrical shock and arc flash hazards throughout your facility. Determine protective boundaries for electrical equipment. NFPA 70E recommends Limited and Restricted Approach Boundaries to protect workers from electric shock, and a separate Arc Flash Boundary to protect them from burns in the event of an arc flash. Employees should keep outside these boundaries during ordinary work.
Identify equipment and components that present a significant risk of arc flash. The NFPA identifies the following types of frequently-affected equipment:
- Switchboards
- Panelboards
- Industrial control panels
- Meter socket enclosures
- Motor control centers
Warning labels that inform workers of potential hazards are a key part of arc flash prevention. The National Electric Code (NEC) Article 110.16 addresses arc flash protection, stating that affected equipment "shall be field marked to warn of potential arc flash hazards...." In addition, NFPA 70E requires that arc flash labels contain information specific to each piece of equipment, detailing the exact hazards that are present.
Pre-printed arc flash labels can be used, although pre-printed labels must be modified in the field to include the required information. A better option is to print custom arc flash labels on-site. Specialized software can track and organize the information for each label, such as available incident energy, approach distances, and required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Labels should be kept legible and up-to-date, since arc flash hazard levels can change any time your electrical system is modified.
3. Make sure that workers are adequately trainedAny employees who will work on electrical equipment need to be aware of the dangers of arc flash, understand the warning labels and signs, and know how to select and use the appropriate PPE. PPE is the last line of defense to protect against injuries. PPE designed to protect against arc flash hazards is called arc-rated (AR) clothing. AR clothing has been tested against exposure to an electric arc, and its AR rating represents the amount of incident energy the clothing can block or absorb. NFPA 70E offers two methods for determining which arc flash PPE will be the most effective for the job at hand.
Incident Energy Analysis: The expected incident energy of an arc flash is calculated for each piece of equipment, according to its actual installation. The incident energy is then used to determine how much protection a worker would need.
Arc Flash PPE Categories: Each piece of equipment is found on a set of tables in the standard. The tables assign one of four categories to the equipment, each requiring a specific set of PPE and having a minimum arc rating for the clothing to be worn.
-
-
Categories 1 and 2 usually require only a single layer of arc-rated PPE, while categories 3 and 4 usually mandate multiple layers of PPE.
-
Think Beyond the Flash
While PPE reduces injuries, the best arc flash safety strategy is prevention. Regular assessments, updated labeling, and consistent training create safer workplaces and reduce downtime.
For facilities looking to improve arc flash safety, DuraLabel®Kodiak®Max Industrial Sign and Label System offers an all-in-one solution. With customizable label templates, durable industrial materials, and seamless integration with LabelForge® PRO, it’s easy to create compliant labels that fit your safety program.
Ready to get started? Download DuraLabel’s free Arc Flash Labeling Quick Start Guide for real-world examples, PPE recommendations, and best practices for improving compliance and workplace safety.
Have questions? Call 1-888-411-3520 to connect with a safety specialist and they will guide you through the process.
Read Next:
What is Arc Flash? A Guide to its Dangers and Safety Measures
The Overlooked Fix That Improves Electrical Panel Safety
Related Resources

Create a Safer Facility with a Proper Arc Flash Boundary
What Is the Arc Flash Boundary? NFPA 70E is the major industrial standard for safe electrical work in the ...
Read
Arc Flash Protection Made Simple for Every Facility
What Is An Arc Flash Protection Boundary? An arc flash protection boundary defines the minimum safe distance ...
Read
Arc Flash Safety in the Workplace: 5 Mistakes to Avoid
How Can Arc Flash Risks Be Identified? Arc flash risks can be identified by evaluating electrical systems, ...
Read.png)
.webp)



%20(1).webp)
